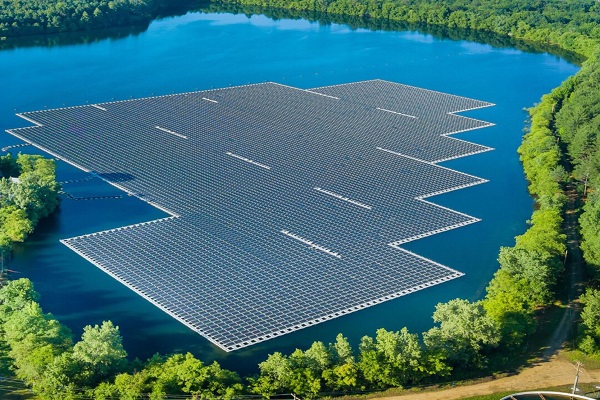

A recent report by market research firm DataM Intelligence indicates that the global floating solar panel market will experience significant growth over the next seven years, driven by land scarcity, mandatory government renewable energy requirements, and the inherent efficiency advantages of the technology. The Asia Pacific region is leading the way for this technology. The floating solar panel market reached $55.11 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to $84.9 million by 2032, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.55% from 2025 to 2032. This growth signifies a transformation in the solar industry: floating photovoltaic (FPV) systems, once a niche application, are becoming a core component of decarbonization strategies in countries with limited land. Global new floating solar capacity reached 1.8 gigawatts in 2024, setting a new annual record. The Asia Pacific region, particularly Japan and China, is leading the global deployment of floating solar technology. In 2024, Japan accounted for 14% of the global market (US$7.7 million), with land scarcity and policy support driving over 70 MW of new installations. The US market size was approximately US$6.4 million (11.6%), with California and Florida promoting the integration of panels with water treatment facilities, and incentive policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act accelerating the development of hybrid energy storage models. In terms of corporate competition, the top five companies, including Ciel & Terre International and Trina Solar, collectively held 64% of the market share in 2024, with Ciel & Terre leading the pack with 1.2 GW of global installed capacity. The report indicates that floating solar power is approaching commercial maturity, and future growth will focus on hybrid systems combining floating solar with hydropower and energy storage to improve grid reliability. Floating solar technology solves two core challenges of large-scale solar deployment: land competition and high power generation demand. Installing panels on artificial water bodies such as reservoirs, hydropower dams, and industrial pools avoids conflicts with agricultural or urban development. The natural cooling effect of water improves panel efficiency by approximately 9% compared to ground-mounted installations, while covering the water surface reduces evaporation, which is of dual value in arid or water-scarce regions. The US, Japan, South Korea, China, India, and some European countries are prioritizing the promotion of this technology, especially in urban or densely populated areas, to achieve renewable energy targets and improve grid stability.
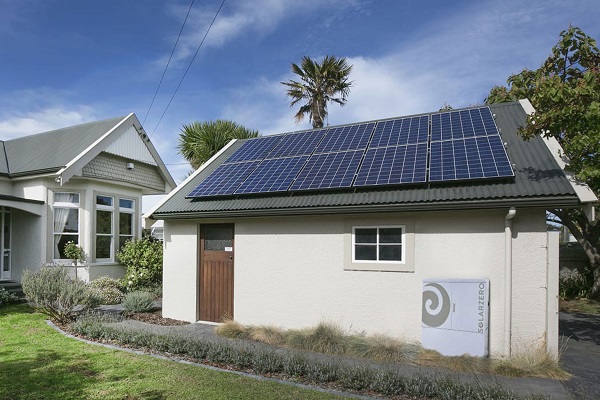

In November 2025, the New Zealand Energy Efficiency and Energy Conservation Agency (EECA) released a significant draft public specification (SNZPAS6014) for residential solar photovoltaic and battery storage systems, open for public comment from that date until October 9, 2025. This is New Zealand's first comprehensive technical guidance document for solar products, marking a new stage in the standardization of the country's clean energy market. The draft specification covers core equipment such as solar panels, inverters, and battery storage systems, aiming to provide consumers with scientific and independent professional advice to help households choose suitable solar systems based on their needs. The specification also details regulatory requirements for grid connection of solar systems and key information such as how to sell excess electricity back to the grid. EECA plans to use this document for compliance guidance in the solar equipment industry, with the technical specification section (Appendix B) listing acceptable standards and related solutions for various systems. This specification comes at a time of rapid development in the New Zealand solar market. By 2024, New Zealand's installed solar capacity had reached 447 megawatts, more than doubling from 224 megawatts in 2022, with over 62,700 solar systems installed nationwide. The New Zealand government has set ambitious targets: to increase the share of renewable energy from 80% to 90% by 2025 and to 95% by 2035. Projections indicate that New Zealand's installed solar capacity will reach 535 megawatts by 2030.

Colombia has approved COP 8.35 trillion ($2.1 billion) for its Colombia Solar program to equip 1.3 million low-income households with PV systems between 2026 and 2030. The Colombian government has approved 83.5 billion pesos (approximately US$2.1 billion) for the "Colombian Solar Plan" from 2026 to 2030, aiming to install rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) systems for about 1.3 million low-income households. The Colombian National Planning Agency (DNP) confirmed that policy document CONPES 4158 approved 83.5 billion pesos for the period 2026-2030 to support an electricity subsidy program for approximately 1.3 million low-income households. This program, part of the "Colombian Solar Plan" led by the Ministry of Mines and Energy and technically supported by the DNP and the Ministry of Finance and Public Credit, aims to replace traditional electricity subsidies with rooftop solar PV self-generation. Project funding will come from public, private, and international partnerships, with implementation handled by grid operators, local governments, and utilities. The project is expected to reduce electricity bills for beneficiary households through solar PV self-generation, while also alleviating financial pressure on the Solidarity Subsidy and Income Redistribution Fund (FSSRI), which incurred a deficit of over 40 billion pesos in 2024. The plan is also expected to create over 25,000 direct and indirect jobs, drive green economic development, and provide renewable energy technology training in key areas, including the “Regional Development Project” areas established after the Colombian government signed a peace agreement with FARC-EP in 2016. Furthermore, the project aligns with recent regulatory reforms, including expedited environmental permitting processes for solar projects ranging from 10 MW to 100 MW, with approval times expected to be reduced by 70%, and optimized assessment criteria based on the characteristics of photovoltaic projects.
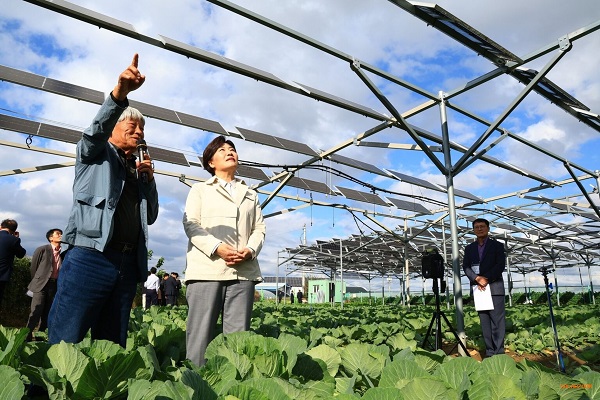

South Korea's Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs plans to draft legislation next year to provide a legal basis for agricultural photovoltaic (PV) projects, aiming to promote the application of solar energy in agriculture. The Ministry announced plans to introduce legislation to provide a legal foundation for agricultural PV projects. Agriculture Minister Song Mi-ryung met with farmers and representatives of solar energy companies this week to discuss the relevant legislation. She stated that the bill is expected to be drafted this year and formally promulgated in the first half of next year. The meeting was held at an agricultural PV demonstration base in Ochang-eup, Cheongju, where cabbage crops were growing under solar panels. Earlier this month, the Ministry of Agriculture stated on its website that the new agricultural PV regulations will prevent overexploitation of projects, ensure food security, and guarantee that profits are returned to residents, communities, and farmers. The new law will be based on rural spatial planning, clearly defining suitable agricultural land for PV deployment. This statement addressed concerns raised by some media outlets regarding future projects. The Ministry added that, as agricultural PV is still in the pilot stage, the media should avoid speculative reporting. The Ministry of Agriculture first proposed an agricultural photovoltaic strategy in April 2024, planning to extend the permit period for idle farmland from 8 years to 23 years. Earlier this year, researchers predicted that solar energy will become South Korea's most cost-competitive energy source between 2030 and 2035.

According to SAPVIA's estimation, South Africa will add approximately 928 MW of new photovoltaic capacity in the first quarter of 2025. This includes 280 MW of projects that have been connected to the grid through the country's flagship "Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Program" (REIPPPP) since December 2024, as well as 647 MW of non-REIPPPP photovoltaic projects. It is expected that the new installed capacity this year will exceed 1.1 GW of 2024. SAPVIA stated that by the middle of 2025, the cumulative installed capacity of photovoltaic power in South Africa is estimated to be 9457 MW. The association said: "As of July 2025, the total scale of photovoltaic projects reached 1.0078 GW, accounting for the vast majority of the total 14.9 GW reserve projects. In addition, there are still 11 REIPPPP projects under construction." REIPPPP is a significant driving force for the large-scale photovoltaic market in South Africa. In July this year, the South African government approved six new photovoltaic projects in the seventh round of procurement, with a total installed capacity of 1290MW. This is the largest commitment for utility-scale photovoltaic projects in South Africa this year.This 1290MW capacity comes from the reallocation of unused indicators for onshore wind power projects. SAPVIA stated: "This strategic move ensures that the unused wind power capacity can be quickly redirected to photovoltaic projects that can be rapidly deployed and connected to the grid, thereby strengthening South Africa's commitment to accelerating its clean energy transition." Apart from REIPPPP, the South African market is gradually adopting a scheme that combines energy storage with renewable energy to enhance grid stability. SAPVIA also pointed out that the industrial and commercial (C&I) market in South Africa has promising prospects. Since June 2024, 100MW-scale projects ranging from 100 kilowatts to 1MW have been registered, and another 250MW-scale projects ranging from 1MW to 50MW have also been filed for approval. In contrast, with the end of "load shedding", the residential photovoltaic market in South Africa has shown signs of slowing down. The association stated: "From the number of new photovoltaic installation companies that have applied for the PV GreenCard membership, this trend is quite obvious, but it is still impossible to quantify at present." Earlier this year, the South African government officially approved the national renewable energy master plan, with the goal of deploying at least 3 GW of new renewable energy annually, and increasing it to 5 GW by 2030. In August this year, the South African state-owned power company Eskom launched a renewable energy power purchase program, targeting large electricity consumers who are interested in signing power purchase agreements. The first round of bidding involved a capacity of 291MW for photovoltaic power.

Recently, the government of Indonesia has announced a new plan, aiming to deploy 100 GW of solar power generation projects. This plan is divided into two parts. It includes 80 GW of distributed photovoltaic power, and the deployment of "1 MW photovoltaic + 4 MWh energy storage" micro-grid systems in 80,000 villages, which will be operated by the village-level cooperative Merah Putih. Additionally, it also includes a 20 GW centralized photovoltaic project plan, covering both grid-connected and off-grid modes. This project aims to reduce the electricity cost in rural areas. The system is expected to have an electricity price of $0.12 - $0.15 per kilowatt-hour, which is lower than the $0.20 - $0.40 per kilowatt-hour for diesel power generation. It also aims to help Indonesia achieve its goal of 108.7 GW of solar energy by 2060 and is planned to be completed within five years. At present, this plan is being jointly promoted by the Ministry of Energy, the Ministry of Economic Coordination, and others.

The role of photovoltaic brackets in photovoltaic systems is to support and fix photovoltaic modules to ensure that they can stably receive sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. At the same time, photovoltaic brackets can also adjust the angle and orientation of photovoltaic modules to improve energy conversion efficiency and protect the modules from damage by the external environment. These functions enable photovoltaic systems to operate more efficiently and reliably, providing people with clean and renewable energy. The photovoltaic bracket foundation is an important part of the photovoltaic bracket system. It provides a solid support for the photovoltaic bracket to ensure that the photovoltaic modules operate safely and stably under various climatic conditions. The selection of photovoltaic bracket foundations needs to be determined according to the geological conditions, climatic conditions and engineering requirements of the installation site. What is the photovoltaic bracket foundation? The photovoltaic bracket independent foundation refers to a basic structure used in photovoltaic power generation systems to support photovoltaic brackets and solar panels, and bear the weight of photovoltaic brackets and solar panels as well as external loads such as wind and snow loads. Therefore, it needs to have sufficient bearing capacity and stability to ensure the safe operation of the photovoltaic power generation system. The foundation forms commonly used by photovoltaic brackets include reinforced concrete independent foundation, reinforced concrete strip foundation, spiral steel pile foundation, reinforced concrete pile column foundation, rock anchor foundation, etc. What is reinforced concrete independent foundation? Reinforced concrete independent foundation is one of the earliest traditional photovoltaic bracket foundation forms, and it is also a foundation form with a wide range of applications. It is a reinforced concrete independent foundation set under the front and rear columns of the photovoltaic bracket, consisting of a foundation bottom plate and a foundation short column above the bottom plate. The top of the short column is set with an embedded steel plate (or embedded bolt) to connect with the upper photovoltaic bracket, which requires a certain burial depth and a certain foundation bottom area; the foundation bottom plate is covered with soil, and the self-weight of the foundation and the gravity of the soil on the foundation are used to resist the upward pull caused by the environmental load, and the larger foundation bottom area is used to disperse the vertical load of the photovoltaic bracket downward, and the friction between the bottom surface of the foundation and the soil and the resistance between the side of the foundation and the soil are used to resist the horizontal load. The advantages of reinforced concrete independent foundation are clear force transmission path, reliable force, wide application range, and ...

A fixed photovoltaic bracket is a bracket that enables the photovoltaic array to receive solar radiation in a fixed manner. When designing a fixed photovoltaic bracket, it is necessary to refer to the local geographical location, environment, climate and other conditions to fix the bracket at an angle that is conducive to receiving sunlight radiation to the greatest extent, and once its position is determined, it usually does not change frequently. Application scenarios and main features of fixed photovoltaic brackets Fixed brackets are widely used in various photovoltaic systems due to their simple structure and low cost. In particular, fixed brackets have more advantages in the following scenarios: Rooftop photovoltaic system: Due to limited roof space and limited load-bearing capacity, fixed brackets are more suitable for installation on the roof. By reasonably designing the structure and layout of the bracket, the roof space can be fully utilized and the power generation efficiency of the photovoltaic system can be improved. Ground photovoltaic power station: When building a photovoltaic power station on an open ground, due to the strong bearing capacity of the foundation and low wind speed, the fixed bracket can also meet the stability and safety requirements of the system. At the same time, through reasonable layout and optimized design, the power generation efficiency and economic benefits of the photovoltaic power station can be further improved. The reason why photovoltaic fixed brackets have a wide range of applications in the photovoltaic market is that they have the following significant features: High stability: The fixed bracket adopts a sturdy structural design, which can remain stable under various climatic conditions and ensure the safe operation of photovoltaic modules. Whether it is a rainy summer or a cold winter, the fixed bracket can reliably support the photovoltaic modules and reduce the risk of module damage caused by the shaking of the bracket. Low maintenance cost: Since the fixed bracket has no moving parts and a simple structure, the maintenance cost is relatively low. Users only need to clean and inspect the photovoltaic modules regularly to ensure the normal operation of the system. Easy installation: The installation process of the fixed bracket is relatively simple, and no complicated debugging and calibration work is required. Users only need to install according to the instructions or the guidance of professionals to quickly complete the construction of the photovoltaic system. Wide applicability: The fixed bracket has low site requirements and is suitable for various sites, including roofs, ground, hillsides, etc. Whether in cities or rural areas, the fixed bracket can be flexibly used. Long life: The service life of the fixed bracket is relatively long, generally reaching more than 30 years.

Despite its war-torn past, Ukraine sees significant growth in its PV market by 2024, with new installed capacity reaching 800-850 MW, according to a report by the Solar Energy Association of Ukraine (ASEU). This growth is mainly driven by businesses and households relying on self-use photovoltaic systems to ensure the stability of electricity supply while addressing grid security challenges. Vladyslav Sokolovsky, chairman of the ASEU board of directors, pointed out that the growth of the self-use market benefited from the abolition of value-added tax (VAT) and tariffs on the import of photovoltaic modules and related equipment in the summer of 2024. This policy provides strong support for the deployment of solar power generation equipment in households and businesses. Even though the war is still going on, ASEU is optimistic about the prospects of Ukraine's photovoltaic market. In the self-generation and self-use market, more companies are investing in photovoltaic systems combined with energy storage to ensure energy security; for industrial photovoltaic projects, some new projects have been announced in 2024, and the construction of industrial photovoltaic power stations is expected to be further promoted in the future. In addition, the Ukrainian government is considering introducing a military risk insurance mechanism for investors, while supporting industry growth through preferential loans and grant projects. According to the National Renewable Energy Action Plan, Ukraine aims to increase its total photovoltaic installed capacity to 12.2GW by 2030.

The UK government’s latest Clean Electricity Action Plan 2030 outlines significant growth in renewable energy capacity by 2030, with a focus on offshore wind and solar photovoltaic (PV) power. The plan sets a target of 45-47GW for solar PV capacity in 2030, emphasizing the potential to exceed the 47GW cap. As of the second quarter of 2024, the UK’s cumulative solar PV capacity stood at 16.6GW, with an additional 23.8GW of projects under construction or signed. Solar Energy UK believes the 45GW target is conservative and that solar PV has the potential to significantly surpass this level. The plan includes promoting solar installations on warehouses, industrial sites, and outdoor parking lots, with a survey on PV canopies for parking lots set to begin in 2025. Additionally, solar technology is included in policies such as the Warm Homes Local Grant and Warm Homes Social Housing Fund, and its application will be further expanded in future versions of the plan. Wind power is also a core component of the plan, aiming for a cumulative installed capacity of 43-50GW by 2030, with onshore wind contributing 27-29GW. Flexible power regulation is also part of the plan, with installations of 23-27GW of battery storage and 4-6GW of long-duration storage planned, along with the development of flexible technologies such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) and hydrogen energy. Furthermore, around 35GW of natural gas storage capacity will ensure secure electricity supply.
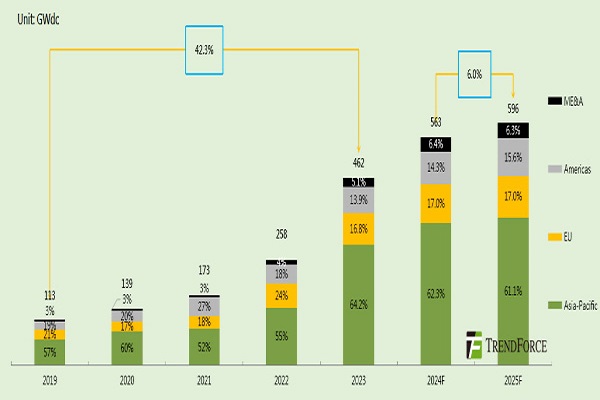
Against the backdrop of global energy transformation, the photovoltaic industry has taken off, and the scale of global photovoltaic installed capacity continues to grow. TrendForce predicts that global photovoltaic installed capacity will reach 596GW in 2025, up 6.0% year-on-year, and the growth rate will slow down significantly. The share of the three major mainstream incremental markets in China, Europe and the United States will decline, and emerging markets such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East will perform well, injecting new impetus into the growth of global photovoltaic installed capacity. Global new installed capacity to reach 596GW in 2025 According to TrendForce data, global photovoltaic installed capacity has grown rapidly from 113GW in 2019 to 462GW in 2023, with an average annual compound growth rate of 42.3%. After experiencing high growth in the first five years, it is expected that the growth rate of global photovoltaic installed capacity will drop sharply from 2025 and enter the adjustment stage. In 2025, global photovoltaic installed capacity will reach 596GW, up 6.0% year-on-year. In terms of market share, the Asia-Pacific market fell slightly to 61.1%, the Americas market grew to 15.6%, and the market share of Europe and the Middle East and Africa did not change much. From the data of new photovoltaic installations in the four major regional markets in 2025, the Americas will lead slightly in growth, and the Asia-Pacific region will still lead in growth. In 2025, driven by the two major markets of the United States and Brazil, the Americas will maintain its leading growth rate; the emerging countries in the Middle East and Africa are still to be developed, and the growth rate has slowed down significantly; the Asia-Pacific region leads the global photovoltaic market in growth, but the growth rate of installed capacity has slowed down under the high base; Europe has steadily increased its growth under the overall goal of coal withdrawal and renewable energy.

The German Federal Solar Industry Association issued a communiqué on January 6, 2025, stating that by the end of 2024, Germany's total installed capacity of solar power generation exceeded 100 GW for the first time. In 2024, 14% of Germany's electricity consumption was provided by solar systems, an increase from 12% in 2023. The communiqué showed that Germany's solar industry continued to grow in 2024, with more than 1 million new solar power generation systems and 17 GW of new installed capacity, an increase of about 10% over 2023. The main driving force for the growth of solar power generation in 2024 came from ground-based photovoltaic power stations, with an additional installed capacity of 6.3 GW, an increase of about 40% over the previous year. The data also showed that the growth of solar systems installed on residential roofs slowed down, while solar systems installed on corporate roofs and residential balconies increased rapidly. Germany plans to achieve at least 80% of its electricity consumption from renewable energy by 2030. To achieve this goal, the total installed capacity of solar power generation needs to reach 215 GW. Carsten Koenig, head of the German Federal Solar Industry Association, said: "If the market growth continues to maintain a similar scale in the next two years, we will enter the sprint stage."